I. Introduction to Hydraulic Shearing Machine Specifications
Hydraulic shearing machines are indispensable tools in the metalworking industry, used for cutting sheet metal and plate materials with precision and efficiency. These machines, which include types such as guillotine and swing beam shears, leverage hydraulic power (fluid power) to generate the force necessary to shear through metal, making them essential for various manufacturing and fabrication processes.
Understanding the hydraulic shearing machine specifications is crucial. By understanding the specifications and features of hydraulic shearing machines, you can select the right equipment for your specific needs. Consider factors such as cutting capacity, blade material, hydraulic system power, and safety features to ensure operational efficiency and safety.
II. Machine Components and Their Specifications
Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system is the powerhouse of the shearing machine, providing the necessary force to operate the blades. Key specifications include:
- Hydraulic Pressure: Determines the force exerted during cutting. Higher pressure is necessary for cutting thicker or harder materials.
- Flow Rate: Affects the speed of operations. A well-calibrated flow rate ensures efficient performance without causing undue stress on components.
- Pump Type: Vane, gear, or piston pumps are commonly used, each offering different levels of efficiency and durability based on application needs.
Different types of hydraulic fluids are used depending on the machine's specifications and operating conditions. The choice of fluid can significantly impact the machine's performance and longevity.
Shearing Blades
The blades are pivotal to the shearing process, supported by their specific design and material choices:
- Blade Mounting System: Ensures stability during operation. Quick-change systems allow for fast blade replacements, minimizing downtime.
- Blade Holders: Must securely support the blades and allow for precise adjustments to maintain optimal cutting angles and clearances.
Frame and Structure
The structural integrity of the machine’s frame directly impacts its stability and precision. Critical elements include:
- Material and Design: Frames are typically made from high-strength steel to withstand significant stress. Advanced designs incorporate vibration dampening features to enhance precision.
- Reinforcement: Reinforced frames support higher cutting capacities, ensuring consistent performance during heavy-duty operations.
Control Systems
Modern hydraulic shearing machines incorporate advanced control systems for enhanced operational flexibility and safety:
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI): Provides intuitive control, making it easier for operators to monitor and adjust machine settings in real-time.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): Facilitate automation of settings like stroke rate, cutting angle, and blade clearance.
Pressing Device
The pressing device plays a critical role in maintaining the quality and accuracy of the cuts. It includes:
- Hydraulic Pressing Plate: Positioned in front of the frame, it holds the material firmly in place during the shearing process, preventing any movement that could compromise the cut's precision.
Back Gauge Mechanism
The backgauge system adjusts the position of the material for precise cutting. Important features include:
- Precision Control: Often automated for high accuracy, allowing precise positioning and repeatability of cuts.
- Range: Determines the maximum size of materials that can be handled efficiently, aligning with the cutting length capabilities of the machine.
Safety Mechanisms
Safety is paramount to prevent accidents and protect operators:
- Guarding and Interlocks: Physical barriers and electronic interlocks prevent access to hazardous areas during operation.
- Emergency Stop Functions: Easily accessible and responsive, allowing operators to quickly halt operations in case of an emergency.
Lubrication System
A well-designed lubrication system ensures the longevity of moving parts:
- Automated Lubrication: Delivers consistent lubrication to critical components, reducing wear and maintenance needs.
- Type of Lubricant: Selected based on machine usage and environmental conditions to optimize performance and minimize friction.
Electrical Unit
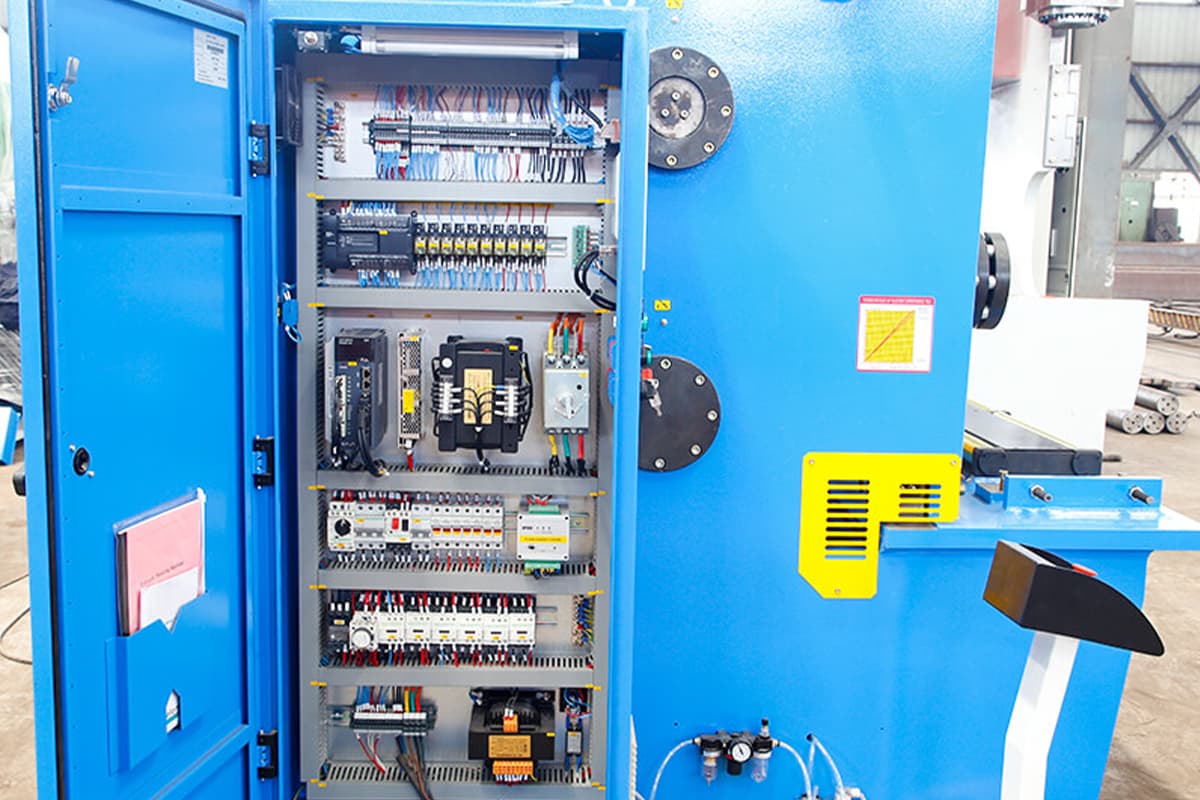
The electrical system supports all machine operations and must be reliable and efficient:
- Wiring and Circuit Protection: Designed to handle power loads typical for industrial environments, with safeguards against overloads and short circuits.
- Energy Efficiency: Machines with energy-efficient components reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
III. Essential Specifications to Consider
Understanding Cutting Capacity
The cutting capacity of a hydraulic shearing machine refers to the maximum thickness and length of material that the machine can cut. This specification is critical as it determines the range of materials you can work with. Cutting capacity is often expressed in terms of material thickness (e.g., up to 20mm) and length (e.g., up to 4000mm).
Maximum Cutting Thickness
The maximum cutting thickness varies depending on the material being processed:
- Mild Steel: Typically ranges from 6mm to 40mm
- Stainless Steel: Generally 60-70% of mild steel capacity
- Aluminum: Often 150-200% of mild steel capacity
For instance, a machine rated for 12mm mild steel might handle up to 8mm stainless steel or 20mm aluminum.
Maximum Cutting Length and Width
Cutting length capabilities typically range from 2000mm to 6000mm, with some specialized machines offering even greater lengths. Width is usually determined by the machine's throat depth, which can vary from 750mm to 1500mm or more.
Capacity Variations
Capacity can vary significantly across manufacturers and models. For example:
- Entry-level machines: 6mm x 2500mm
- Mid-range machines: 16mm x 4000mm
- Heavy-duty machines: 32mm x 6000mm
Machine Dimensions and Weight

Understanding the physical specifications of hydraulic shearing machines is crucial for installation planning and workspace optimization.
Overall Dimensions
Typical dimensions for a mid-range machine (e.g., 16mm x 4000mm capacity):
- Length: 5000-5500mm
- Width: 2200-2500mm
- Height: 2000-2300mm
These dimensions can vary based on additional features like extended material support tables or advanced control systems.
Working Area Dimensions
The working area is typically slightly smaller than the overall machine dimensions:
- Table length: Usually matches the maximum cutting length
- Throat depth: Ranges from 750mm to 1500mm, affecting the maximum sheet width that can be processed
Weight Considerations
- Net weight: Can range from 10,000 kg for smaller machines to over 50,000 kg for large, heavy-duty models
- Gross weight: Includes additional components and packaging, typically 10-15% higher than net weight
Installation considerations:
- Floor load capacity assessment
- Transportation logistics
- Crane or forklift requirements for positioning
Hydraulic System
The hydraulic system is the heart of these machines, providing the power necessary for precise and efficient cutting operations.
Operating Pressure Ranges
- Typical range: 20-35 MPa (2900-5075 psi)
- Higher pressures generally correlate with increased cutting capacity and speed
- Pressure adjustment capabilities allow for optimizing performance across different materials and thicknesses
Oil Tank Capacity and Hydraulic Fluid
- Tank capacity: Usually ranges from 200 to 1000 liters, depending on machine size
- Hydraulic fluid: ISO VG 46 or 68 hydraulic oils are common, with growing interest in biodegradable options for environmental compliance
Main Motor Power
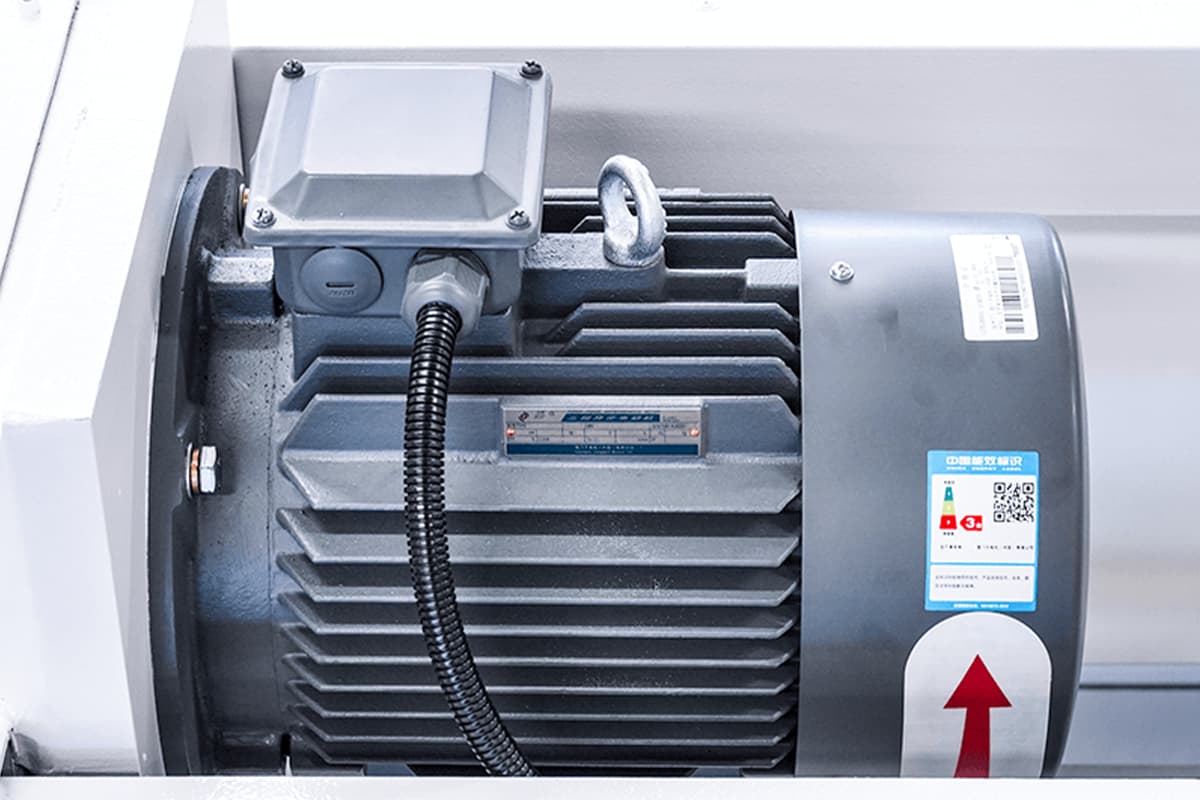
- Power range: 15 kW to 75 kW or more
- Direct correlation with cutting capacity and speed
- Energy-efficient designs incorporating variable frequency drives (VFDs) are becoming standard
Pump Specifications
- Types: Axial piston pumps are most common, with some machines using variable displacement pumps for energy efficiency
- Flow rates: Typically 100-300 L/min, adjusting based on cutting requirements
- Efficiency: Modern pumps achieve 90-95% efficiency, contributing to overall machine performance and energy savings
Electrical Specifications
Electrical specifications are critical for ensuring proper machine operation and integration into existing power systems.
Power Requirements
- Voltage: 380-480V AC, 3-phase (common in industrial settings)
- Frequency: 50/60 Hz, with some machines offering dual-frequency compatibility
- Current draw: Varies based on motor size and auxiliary systems
Control System Specifications
- PLC types: Siemens, Allen-Bradley, and Mitsubishi are popular choices
- Software versions: Regularly updated for improved functionality and cybersecurity
- HMI (Human-Machine Interface): Typically touchscreen, ranging from 10" to 19" displays
Electrical Safety Features
- Emergency stop circuits: Category 0 (immediate power disconnection) and Category 1 (controlled stop then power disconnection)
- Overload protection: Circuit breakers and thermal overload relays
- Safety interlocks: Prevent operation when guards are open
- Compliance standards: IEC 60204 for electrical equipment of machines, UL 508A for industrial control panels
The Importance of Blade Material and Length
The length and material of the shearing blades are crucial for achieving precise and clean cuts. Blade length should match your cutting requirements, while blade material affects durability and cutting performance.
- Blade Length:Â Typically ranges from 1000mm to 6000mm, depending on the machine's design and intended use. Matches or slightly exceeds the machine's cutting length.
- Blade Material:
- High-Speed Steel (HSS):Â Offers excellent durability and sharpness, making it suitable for high-precision applications. For example, HSS blades are ideal for cutting thin sheets of stainless steel with minimal burring.
- Carbide:Â Harder and more wear-resistant, making it ideal for cutting abrasive materials. For instance, carbide blades can efficiently cut through hardened steel or composite materials with high wear resistance.
- Blade Thickness: 20-50mm, depending on machine capacity.
- Number of Cutting Edges: Usually 4, allowing for rotation to extend blade life.
- Blade Hardness: Typically 58-62 HRC.
Cutting Angle and Stroke Rate
The cutting angle and stroke rate directly influence the cutting quality and efficiency of the hydraulic shearing machine.
- Cutting Angle:Â The angle at which the blade meets the material. Adjustable cutting angles allow for more versatility and can improve cutting precision.
- Fixed angle: Common in smaller machines, typically 1-3 degrees
- Adjustable angle: 0.5-2.5 degrees, allows optimization for different materials and thicknesses
- Typical ranges: Thin materials (< 3mm): 1-1.5 degrees; Medium thickness (3-10mm): 1.5-2 degrees; Thick materials (> 10mm): 2-2.5 degrees
- Example:Â A smaller cutting angle (e.g., 1-2 degrees) provides a cleaner cut but may require more force. This is beneficial for cutting thin, delicate materials where precision is critical.
- Stroke Rate:Â The number of cutting strokes the machine can perform per minute. Higher stroke rates increase productivity but may impact the stability and precision of the cuts.
- Example:Â A stroke rate of 30 strokes per minute may be suitable for a high-volume production line, whereas a lower stroke rate may be preferable for precision work.
Throat Depth
Throat depth refers to the distance between the cutting edge and the back of the machine's frame. This specification determines the maximum width of the material that can be fed into the machine without obstruction.
- Standard Throat Depth:Â Suitable for most general-purpose cutting tasks.
- Example:Â For typical sheet metal work, a standard throat depth allows for adequate maneuverability and flexibility.
- Extended Throat Depth:Â Required for cutting wider materials or when working with complex shapes.
- Example:Â An extended throat depth is ideal for fabricating large components for automotive or aerospace applications where wider sheets are common.
Backgauge Range
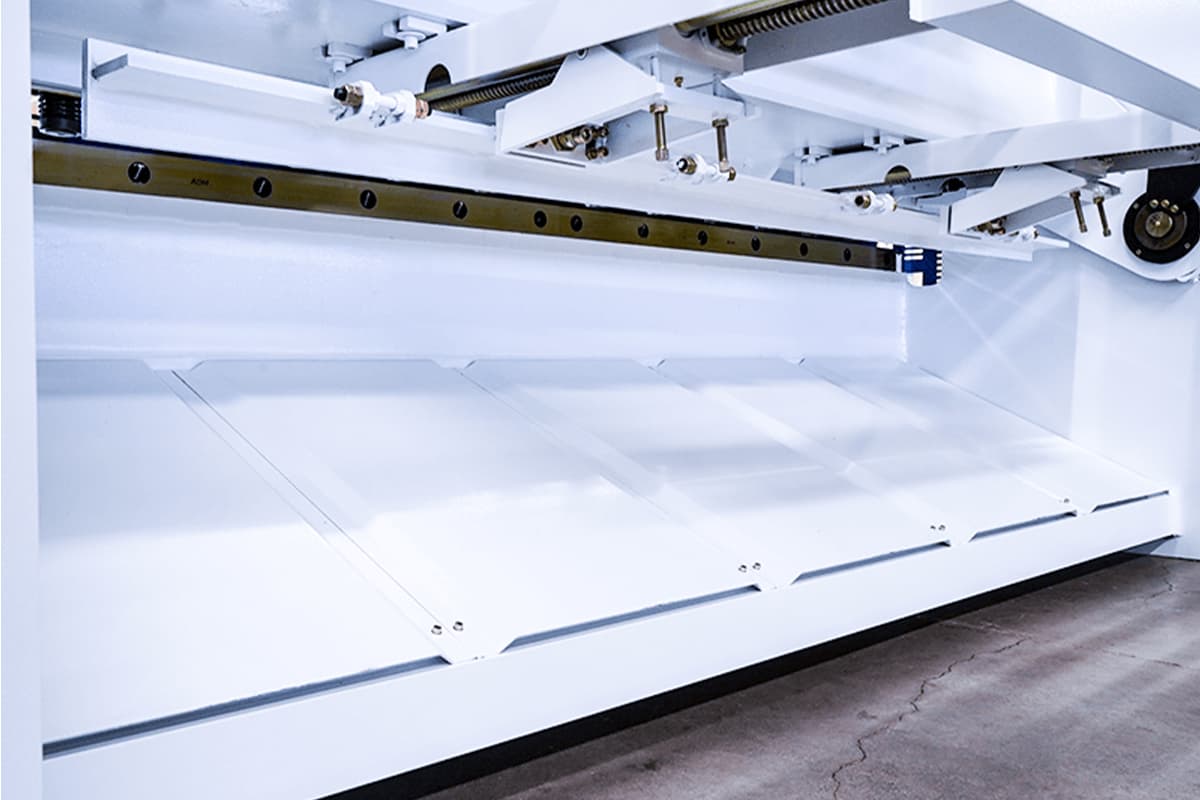

The backgauge mechanism positions the material accurately before cutting, and its range determines the maximum distance it can move to accommodate different material sizes.
- Backgauge Range:Â Typically ranges from 500mm to 1000mm or more. A larger backgauge range allows for greater versatility in material positioning and enhances cutting precision.
- Example:Â For a sheet metal shop that handles a variety of material sizes, a backgauge range of 1000mm provides the flexibility needed for diverse cutting tasks.
- Adjustability:Â Look for machines with easily adjustable backgauges, preferably with digital displays or CNC controls for precise positioning.
- Example:Â CNC-controlled backgauges can significantly improve efficiency and accuracy in a high-precision manufacturing environment.
IV. Selecting the Right Machine for Your Needs
Assessing Your Specific Requirements
Understanding your specific requirements is the first step in selecting the right hydraulic shearing machine. This involves evaluating material types, production volumes, precision requirements, and budget considerations.
Material Type and Thickness
- Material Type:Â Determine the primary materials you will be cutting (e.g., mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum). Different materials require different blade materials and machine capabilities.
- Material Thickness:Â Identify the maximum and minimum thickness of the materials. This helps ensure the machine's cutting capacity matches your needs.
Example:Â A manufacturing company specializing in aluminum parts chose a hydraulic shearing machine with carbide blades to handle various thicknesses, resulting in improved cutting quality and reduced blade wear.
Production Volume
- High-Volume Production:Â Look for machines with high cutting speeds and robust construction to handle continuous operation.
- Low to Medium Volume:Â A machine with moderate cutting speed and simpler controls can be cost-effective for lower production volumes.
Example:Â A small fabrication shop opted for a machine with moderate speed and basic controls, balancing cost and functionality effectively.
Precision Requirements
- High Precision:Â For intricate cuts, consider machines with CNC (Computer Numerical Control) or NC (Numerical Control) systems that offer programmable operations and enhanced accuracy.
- General Precision:Â Standard hydraulic shearing machines with manual or basic digital controls may suffice for less precise tasks.
Example:Â A precision engineering firm integrated a CNC hydraulic shearing machine into their operations, achieving high repeatability and intricate cuts for complex components.
Budget Considerations
- Initial Cost:Â Evaluate the upfront cost of the machine and ensure it fits within your budget.
- Operational Costs:Â Consider long-term costs, including maintenance, energy consumption, and blade replacements.
Tip:Â Investing in a slightly higher-capacity machine can provide flexibility for future growth and accommodate a wider range of materials.
Comparing Different Models and Brands
Comparing different models and brands involves evaluating machine features, capabilities, and the reputation of manufacturers.
Machine Features and Capabilities
- Cutting Capacity:Â Ensure the machine's cutting capacity aligns with your material thickness and length requirements.
- Blade Material and Length:Â Choose the appropriate blade material (e.g., high-speed steel or carbide) and length for your tasks.
- Control Systems:Â Evaluate CNC or NC control systems for programmable operations and enhanced precision.
Example:Â A large-scale metalworking company selected a machine with high-speed steel blades and CNC controls, enabling efficient processing of varied material thicknesses with high precision.
Brand Reputation and Support
- Reputation:Â Research manufacturers with a history of producing reliable and high-quality machines.
- Support and Service:Â Consider after-sales support, including maintenance services, spare parts, and technical assistance.
V. FAQs
1. What is the difference between swing beams and guillotine shears?

| Feature | Swing Beam Shears | Guillotine Shears |
| Cutting Mechanism | Pivoting upper beam that swings to cut | Vertical movement of the upper blade |
| Precision | Moderate precision, suitable for general use | High precision,ideal for straight and clean cuts |
| Material Thickness | Thinner to medium-thickness sheets | Capable of cutting thicker and tougher materials |
| Applications | General fabrication,lighter manufacturing | Heavy-duty applications like shipbuilding |
| Ease of Use | Easier to operate with simpler controls | More complex, requiring skilled operators |
2. Are there specific safety standards for operating hydraulic shearing machines?
Yes, operating hydraulic shearing machines involves adhering to specific safety standards to protect operators and ensure safe operation. Key standards include:
- OSHA 1910.212: Mandates machine guarding to protect operators from hazards.
- ANSI B11.4-2003: Provides safety requirements for the construction, care, and use of shearing machines.
- CE Marking (for Europe): Ensures the machine meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection requirements.
3. How does blade material affect the performance of a hydraulic shearing machine?
The material of the shearing blades significantly impacts cutting performance and durability:
- High-Speed Steel (HSS): Offers excellent sharpness and durability, making it suitable for high-precision applications and cutting thin sheets with minimal burring.
- Carbide: Known for its hardness and wear resistance, carbide blades are ideal for cutting abrasive materials and handling tougher, thicker sheets.
Specialty Resins,Adsorbent Resin,Anion Exchange Adsorbent Resin,Catalytic Resin
Henan Comcess Industry Co., Ltd. , https://www.comcessresins.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)